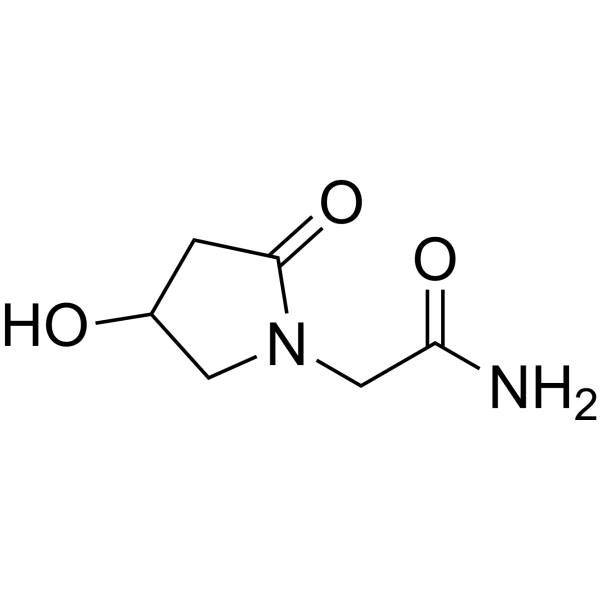
Why does product quality matter so much with oxiracetam? Since the
compound isn't regulated as a pharmaceutical drug in most jurisdictions,
quality control varies dramatically between suppliers. Poor-quality
products may contain incorrect concentrations (rendering dosing
calculations useless), contaminants from inadequate manufacturing
processes, or even entirely different substances mislabelled as
oxiracetam. The presence of heavy metals, solvent residues, or bacterial
contamination poses genuine health risks that extend well beyond simply
getting an ineffective product.
What should you look for when evaluating oxiracetam suppliers? Reputable
vendors provide Certificates of Analysis (COA) from independent
third-party laboratories—not in-house testing—confirming purity greater
than 98%, typically measured by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
(HPLC). These COAs should be batch-specific, meaning each production
batch receives its own testing, rather than showing a single certificate
from years ago. The documentation should identify common contaminants
and confirm they're below acceptable thresholds.
Quality Verification Checklist
Third-party COA (Certificate of Analysis)
From independent labs, not manufacturer's internal testing
Purity ≥98% confirmed by HPLC
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography is the gold standard
Batch-specific testing documentation
Each production batch should have its own COA with matching lot
numbers
Heavy metal screening results
Confirmation that lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium are below
limits
Microbial contamination testing
Total plate count, yeast, mould, E. coli, and Salmonella testing
Transparent sourcing information
Details about manufacturing location and Good Manufacturing
Practices (GMP)
How can you verify that a Certificate of Analysis is legitimate? Genuine
COAs include the testing laboratory's name, address, and contact
information, allowing you to independently verify the document's
authenticity if needed. The certificate should show the specific tests
performed (not just "purity: 99%"), the methodology used (like "HPLC" or
"GC-MS"), and the acceptable ranges for each parameter. Be wary of vague
statements or perfectly round numbers—real analytical chemistry produces
specific values like "98.7%" rather than "99.0%".
What's the difference between pharmaceutical-grade and research-grade
oxiracetam? Pharmaceutical-grade compounds meet strict regulatory
standards for human consumption, including extensive documentation of
manufacturing processes, sterility, and excipient purity. Research-grade
(or research chemical grade) means the compound is intended for
laboratory research rather than human consumption, with potentially less
stringent quality controls. In practice, high-quality research-grade
oxiracetam from reputable suppliers can be very pure, but the lack of
pharmaceutical oversight means quality depends entirely on the
supplier's ethics and competence.
Does powder form differ in quality from capsules? Both forms can be
high-quality if sourced from reputable suppliers. Powder offers the
advantage of flexible dosing—you can measure exactly 800mg using a
milligram scale—and typically costs less per dose. Capsules provide
convenience and consistent dosing without requiring scales, but you're
trusting the manufacturer's filling accuracy. Some users prefer powder
for the first purchase to verify the product matches the expected
appearance and taste (oxiracetam has a slightly bitter, chemical taste),
then switch to capsules for daily convenience.
How should oxiracetam be stored to maintain potency? Store it in a cool,
dry place away from direct sunlight, preferably in an airtight
container. Whilst oxiracetam is relatively stable, exposure to moisture,
heat, and light can gradually degrade the compound. Avoid storing it in
bathrooms (humidity) or near windows (temperature fluctuations and UV
exposure). Properly stored oxiracetam should maintain potency for at
least two years from the manufacture date, though most users consume
their supply well within this timeframe.
Are there visual or sensory indicators of quality? High-purity
oxiracetam typically appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder
with a slightly bitter taste. Significant yellowing, clumping (unless
exposed to moisture), or unusual odours may indicate degradation or
contamination. However, sensory evaluation is unreliable for detecting
many contaminants—proper COA verification remains essential. If you're
purchasing capsules, reputable manufacturers use vegetable capsules free
from unnecessary fillers, with minimal excipients listed on the label.
What regulatory categories apply to oxiracetam in different markets? In
the United States, it's typically sold as an unregulated research
chemical or dietary supplement ingredient, occupying a legal grey area.
The UK doesn't control it under the Misuse of Drugs Act, but it's not
approved as a medicine—personal import for own use generally goes
unchallenged by authorities. European countries vary, with Italy and
some others allowing it as a prescription pharmaceutical. Australia and
New Zealand classify it as prescription-only. Before purchasing,
verify your local regulations
and understand that legal status can change. For those exploring
cognitive enhancement, understanding
quality indicators and supplement label requirements
protects both your health and legal standing. Always source from
reputable suppliers.