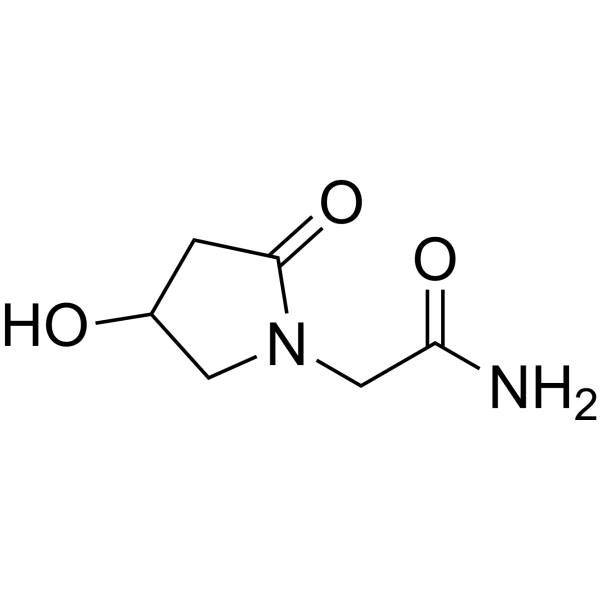
Oxiracetam is a synthetic derivative of piracetam, classed within the racetam family, and developed to provide stronger pro‑cognitive effects at moderate doses. It is typically used in doses between 800 and 2,400 mg per day in divided administrations, and has been studied in dementia, traumatic brain injury, and vascular cognitive impairment.
From our perspective, what makes oxiracetam interesting is not just anecdotes, but the convergence of pharmacology, brain imaging, and behavioral data. When we look at how oxiracetam works, we see a drug that subtly reshapes excitatory and cholinergic signaling and improves energy handling in vulnerable brain regions, especially the hippocampus and cortex.